RPA vs. AI: Understanding the Key Differences
The terms Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion. While both technologies aim to automate tasks, they differ significantly in their approach and capabilities. This article will clarify the distinctions between RPA and AI, helping you understand their unique strengths and applications.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
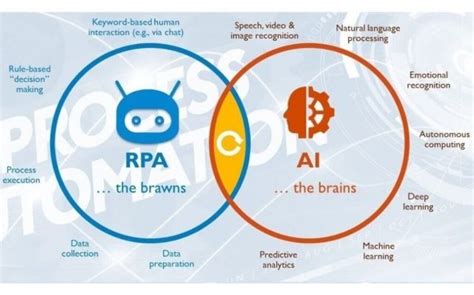
RPA is a technology that uses software robots, or "bots," to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. These bots mimic human actions, interacting with applications and systems in the same way a human would. Think of them as digital assistants that follow pre-defined instructions.
Key Characteristics of RPA:
- Rule-based: RPA excels at tasks with clear, predefined rules and processes. It struggles with exceptions or situations requiring judgment.
- Repetitive tasks: RPA is most effective when automating tasks that are performed repeatedly and consistently.
- Structured data: RPA works best with structured data, such as data in spreadsheets or databases. It has limited capabilities with unstructured data like images or text documents.
- Limited decision-making: RPA bots cannot make decisions on their own. They follow pre-programmed instructions and lack the ability to learn or adapt.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is a broader concept encompassing various technologies that enable machines to mimic human intelligence. AI systems can learn, reason, problem-solve, and adapt to new situations. This contrasts sharply with RPA's rigid rule-following approach.
Key Characteristics of AI:
- Learning and adaptation: AI systems can learn from data and improve their performance over time. They can adapt to changing circumstances and handle exceptions.
- Decision-making: AI can make decisions based on data analysis and learning. This enables automation of complex tasks that require judgment and problem-solving.
- Unstructured data handling: Advanced AI systems can process and understand unstructured data, such as images, text, and audio.
- Predictive capabilities: AI can analyze data to predict future outcomes and proactively take action.
Key Differences Summarized:
| Feature | RPA | AI |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Type | Rule-based, repetitive tasks | Intelligent automation, complex tasks |
| Data Handling | Structured data | Structured and unstructured data |
| Decision-Making | Limited, pre-programmed instructions | Advanced, learning and adaptation |
| Learning Ability | No learning capability | Learns from data and adapts |
| Complexity | Relatively simple to implement | Can be complex to implement and manage |
RPA and AI: A Synergistic Relationship
While distinct, RPA and AI can work together synergistically. AI can enhance RPA by providing capabilities like intelligent decision-making, exception handling, and improved data processing. For example, an RPA bot might handle data entry, while an AI system verifies the data's accuracy and flags any discrepancies. This combination creates a powerful automation solution capable of handling more complex and diverse tasks.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between RPA and AI is crucial for businesses looking to automate processes. While RPA excels at automating repetitive tasks, AI provides the intelligence and adaptability needed for more complex scenarios. The most effective approach often involves leveraging both technologies to create a robust and efficient automation solution. Choosing the right technology depends on the specific needs and complexity of the task at hand.