Robotic Process Automation (RPA) vs. Artificial Intelligence (AI): A Complete Recipe for Understanding the Difference
The terms "Robotic Process Automation" (RPA) and "Artificial Intelligence" (AI) are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion. While both technologies aim to automate tasks, they differ significantly in their approach and capabilities. This article will provide a complete recipe for understanding their distinctions, helping you choose the right tool for your specific needs.
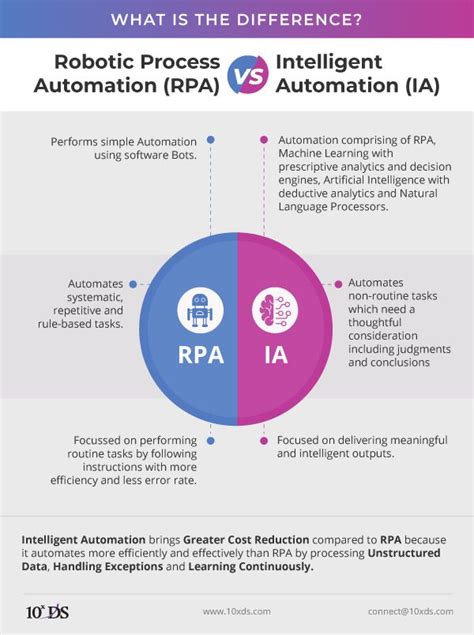
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA is a technology that automates repetitive, rule-based tasks typically performed by humans. Think of it as a digital worker that mimics human actions, such as data entry, filling forms, and moving files. RPA robots follow pre-programmed instructions, executing tasks with high precision and speed.
Key characteristics of RPA:
- Rule-based: Relies on predefined rules and structured data.
- Repetitive tasks: Ideal for automating processes that involve repetitive actions.
- High precision: Minimizes errors associated with manual work.
- Easy to implement: Relatively quick and straightforward deployment.
- Limited decision-making: Cannot make independent decisions or adapt to unexpected situations.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI is a broader field encompassing technologies that enable machines to mimic human intelligence. This includes learning from data, solving problems, and making decisions. AI systems can adapt to new information and improve their performance over time. AI powers many advanced features, including:
- Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms that allow systems to learn from data without explicit programming.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of ML using artificial neural networks to analyze complex data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Computer Vision: Allows computers to "see" and interpret images and videos.
RPA vs. AI: A Detailed Comparison
| Feature | RPA | AI |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Automates rule-based tasks | Enables intelligent decision-making |
| Data Handling | Structured data | Structured and unstructured data |
| Learning | No learning; follows pre-defined rules | Learns from data and improves over time |
| Decision-Making | Limited decision-making capabilities | Capable of independent decision-making |
| Adaptability | Limited adaptability | Highly adaptable |
| Complexity | Relatively simple to implement | Can be complex to implement and manage |
When to Use RPA and When to Use AI
The choice between RPA and AI depends on the specific task and your business needs.
Use RPA for:
- High-volume, repetitive tasks: Data entry, invoice processing, order fulfillment.
- Processes with well-defined rules: Tasks with clear, consistent steps.
- Quick automation needs: RPA offers faster implementation compared to AI.
Use AI for:
- Complex decision-making: Fraud detection, customer service chatbots, predictive maintenance.
- Tasks requiring unstructured data processing: Analyzing text, images, or audio.
- Situations requiring adaptability: AI systems can adjust to changing conditions.
The Synergistic Power of RPA and AI
The true potential lies in integrating RPA and AI. Intelligent Automation, which combines both technologies, leverages the strengths of each. RPA handles the routine tasks while AI provides the intelligence and decision-making capabilities, creating a powerful automation solution.
Conclusion
RPA and AI are distinct yet complementary technologies. Understanding their differences and how they can work together is key to leveraging their power for increased efficiency and productivity. By carefully considering your specific requirements, you can choose the right technology or combination of technologies to optimize your processes and achieve your business goals. This comprehensive guide provides a strong foundation for making informed decisions about implementing these transformative technologies.